In the fast-paced world of display technologies, the past week has witnessed significant developments, especially in the realm of Liquid Crystal Displays (LCDs). Once hailed as a revolutionary leap forward in display technology, LCDs are now facing competition from newer technologies like Organic Light-Emitting Diodes (OLEDs) and Quantum Dot LEDs (QLEDs). This article delves into the key events and advancements of the week, shedding light on how these technologies are shaping the future of visual displays.

I. The Foundation: How LCDs Work
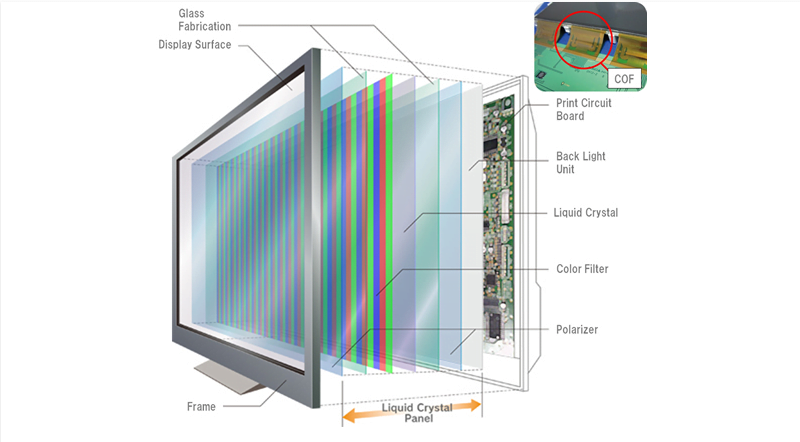
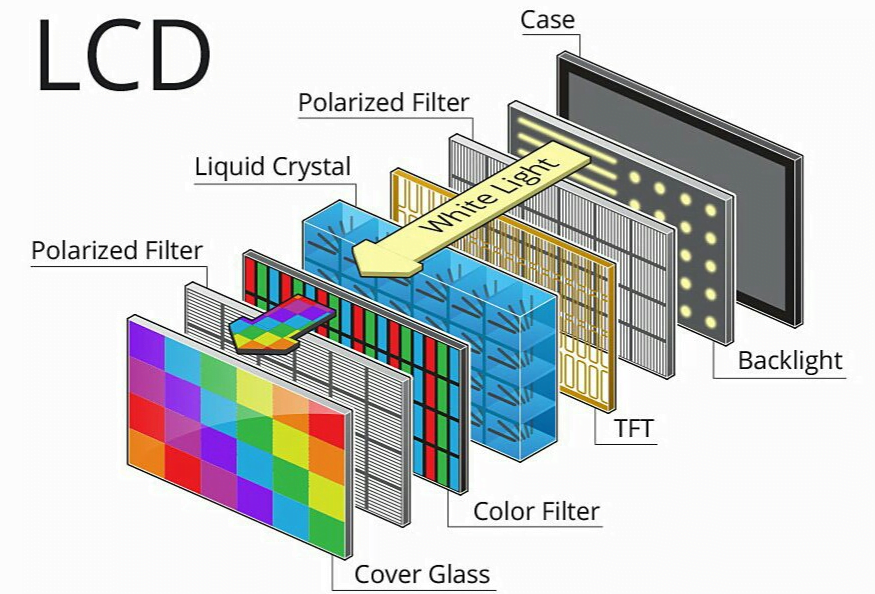
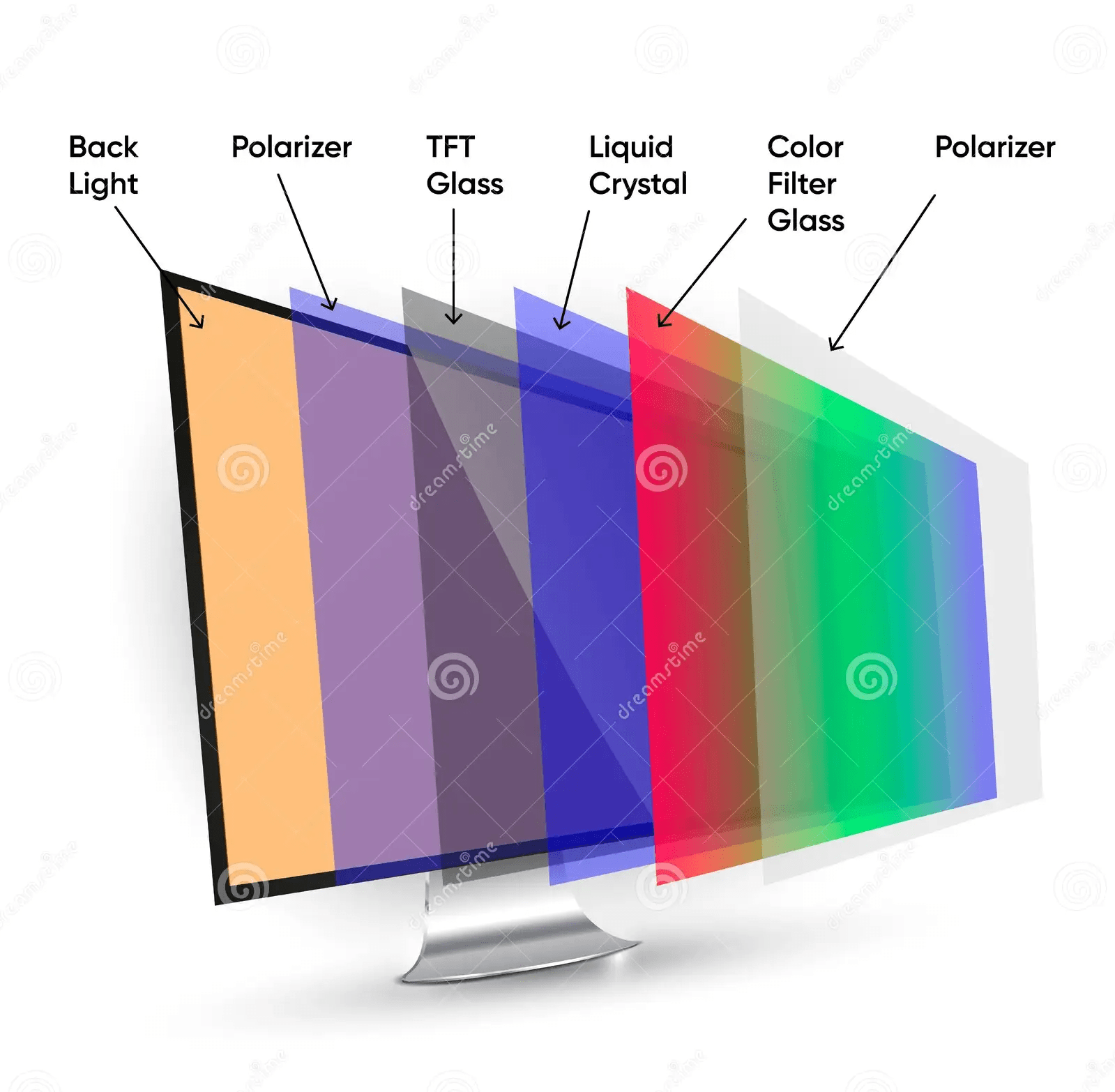
- Overview of LCD Technology:
- LCDs, or Liquid Crystal Displays, are a type of flat panel display that employs liquid crystals in its primary operation.
- Replaced older technologies such as LED and gas-plasma displays due to their thinner design and lower power consumption.
- Pixel Control Mechanism:
- A display consists of millions of pixels, each made up of three subpixels (red, blue, and green).
- Pixels are controlled differently in various display types: CRT, LED, LCD, and newer technologies.
- LCDs use liquid crystals to rotate polarized light and can be either passive matrix or active matrix (TFT) displays.
II. Types of LCDs
- Twisted Nematic (TN):
- Inexpensive with high response times.
- Limitations include low contrast ratios, viewing angles, and color contrasts.
- In-Panel Switching (IPS) Displays:
- Boast better contrast ratios, viewing angles, and color contrasts compared to TN LCDs.
- Vertical Alignment Panels (VA Panels):
- Positioned as a medium quality between TN and IPS displays.
- Advanced Fringe Field Switching (AFFS):
- Top performer in color reproduction compared to IPS displays.
III. LCDs vs OLEDs vs QLEDs

- Shift Towards OLED Technology:
- OLEDs use a single glass or plastic panel, making devices thinner and offering deeper blacks.
- Avoids light leakage issues and provides better contrast and viewing angles.
- Challenges with OLEDs:
- Higher cost and susceptibility to burn-in issues, similar to plasma-based displays.
- Introduction of QLEDs:
- Developed by Samsung, QLEDs enhance traditional LCDs with a quantum dot layer.
- This addition dramatically increases color and brightness compared to standard LCDs.
IV. Making Choices: QLED vs OLED
- QLED Advantages:
- Exceptional brightness without burn-in concerns.
- Improved color and brightness compared to traditional LCDs.
- OLED Strengths:
- Superior contrast ratio and deeper blacks.
- Flexibility in design, demonstrated in smartphones like the Galaxy Fold and iPhone X.
Conclusion: As the dynamic display industry unfolds, LCDs, once the pinnacle of technology, are now sharing the spotlight with OLEDs and QLEDs. The choice between these technologies is nuanced, considering factors like brightness, contrast ratio, and form factor. Stay tuned for the ongoing evolution of visual display technologies, promising continuous innovations that redefine the visual experience for consumers and businesses alike.
[…] Visual Experience: The Xiaomi Pad 6S Pro 12.4 features a stunning 12.4-inch IPS LCD display that serves as a canvas for immersive visual experiences. With a resolution of 2032×3048 […]
[…] the AMOLED technology employed in the display offers several advantages over traditional LCD panels. AMOLED displays are known for their deeper […]
[…] Pova 6 Neo also delivers an immersive viewing experience thanks to its expansive 6.78-inch IPS LCD display. With 1 billion colors and a 120Hz refresh rate, users can enjoy vibrant visuals and smooth […]
[…] is a testament to Apple’s commitment to aesthetics and portability. The Liquid Retina IPS LCD display, spanning 13.0 inches and boasting a resolution of 2048 x 2732 pixels, delivers stunning clarity […]
[…] of the highlights of the iPad Air 11 is its vibrant 11.0-inch Liquid Retina IPS LCD display. With a resolution of 1640 x 2360 pixels and a pixel density of 264 ppi, every image and video […]
[…] Specifications: The Narzo N63 boasts a 6.75-inch IPS LCD display with a 90Hz refresh rate and peak brightness of 560 […]
[…] out as a pinnacle of innovation in the foldable smartphone market. Its advanced design, superior display technology, powerful hardware, and versatile software make it a compelling choice for tech enthusiasts and […]